IRIS beamline at BESSY II extended with nanomicroscopy
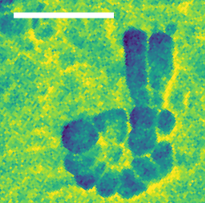
Infrared image of the nucleolus in the nucleus of a fibroblast cell. The scale bar corresponds to 500 nanometres. © HZB
The IRIS infrared beamline at the BESSY II storage ring now offers a fourth option for characterising materials, cells and even molecules on different length scales. The team has extended the IRIS beamline with an end station for nanospectroscopy and nanoimaging that enables spatial resolutions down to below 30 nanometres. The instrument is also available to external user groups.
The infrared beamline IRIS at the BESSY II storage ring is the only infrared beamline in Germany that is also available to external user groups and is therefore in great demand. Dr Ulrich Schade, in charge of the beamline, and his team continue to develop the instruments to enable unique, state-of-the-art experimental techniques in IR spectroscopy.
As part of a recent major upgrade to the beamline, the team, together with the Institute of Chemistry at Humboldt University Berlin, has built an additional infrared near-field microscope.
"With the nanoscope, we can resolve structures smaller than a thousandth of the diameter of a human hair and thus reach the innermost structures of biological systems, catalysts, polymers and quantum materials," says Dr Alexander Veber, who led this extension.
The new nanospectroscopy end station is based on a scanning optical microscope and enables imaging and spectroscopy with infrared light with a spatial resolution of more than 30 nm. To demonstrate the performance of the new end station, Veber analysed individual cellulose microfibrils and imaged cell structures. All end stations are available to national and international user groups.
Funding information: Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung [grant No. project 05K19KH1 (SyMS)]; Germany's Excellence Strategy (grant No. EXC 2008-390540038 – UniSysCat).
arö
https://www.helmholtz-berlin.de/pubbin/news_seite?nid=26746;sprache=en
- Copy link
-
5000th protein structure at BESSY II: Starting point for a COVID drug
Many proteins have a complex architecture that enables biological functions. Molecules can bind to specific sites on a protein and alter its function. A team at HZB has now investigated the Nsp1 protein, which plays a role in infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus. They analysed protein crystals, previously mixed with molecules from a fragment library, and discovered a total of 21 candidates as starting points for drug development. At the same time, they also decoded the 5000th structure at BESSY II.
-
What Zinc concentration in teeth reveals
Teeth are composites of mineral and protein, with a bulk of bony dentin that is highly porous. This structure is allows teeth to be both strong and sensitive. Besides calcium and phosphate, teeth contain trace elements such as zinc. Using complementary microscopy imaging techniques, a team from Charité Berlin, TU Berlin and HZB has quantified the distribution of natural zinc along and across teeth in 3 dimensions. The team found that, as porosity in dentine increases towards the pulp, zinc concentration increases 5~10 fold. These results help to understand the influence of widely-used zinc-containing biomaterials (e.g. filling) and could inspire improvements in dental medicine.
-
Fascinating archaeological find becomes a source of knowledge
The Bavarian State Office for the Preservation of Historical Monuments (BLfD) has sent a rare artefact from the Middle Bronze Age to Berlin for examination using cutting-edge, non-destructive methods. It is a 3,400-year-old bronze sword, unearthed during archaeological excavations in Nördlingen, Swabia, in 2023. Experts have been able to determine how the hilt and blade are connected, as well as how the rare and well-preserved decorations on the pommel were made. This has provided valuable insight into the craft techniques employed in southern Germany during the Bronze Age. The BLfD used 3D computed tomography and X-ray diffraction to analyse internal stresses at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (HZB), as well as X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy at a BESSY II beamline supervised by the Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung (BAM).
