IRIS beamline at BESSY II extended with nanomicroscopy
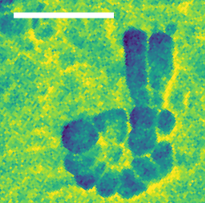
Infrared image of the nucleolus in the nucleus of a fibroblast cell. The scale bar corresponds to 500 nanometres. © HZB
The IRIS infrared beamline at the BESSY II storage ring now offers a fourth option for characterising materials, cells and even molecules on different length scales. The team has extended the IRIS beamline with an end station for nanospectroscopy and nanoimaging that enables spatial resolutions down to below 30 nanometres. The instrument is also available to external user groups.
The infrared beamline IRIS at the BESSY II storage ring is the only infrared beamline in Germany that is also available to external user groups and is therefore in great demand. Dr Ulrich Schade, in charge of the beamline, and his team continue to develop the instruments to enable unique, state-of-the-art experimental techniques in IR spectroscopy.
As part of a recent major upgrade to the beamline, the team, together with the Institute of Chemistry at Humboldt University Berlin, has built an additional infrared near-field microscope.
"With the nanoscope, we can resolve structures smaller than a thousandth of the diameter of a human hair and thus reach the innermost structures of biological systems, catalysts, polymers and quantum materials," says Dr Alexander Veber, who led this extension.
The new nanospectroscopy end station is based on a scanning optical microscope and enables imaging and spectroscopy with infrared light with a spatial resolution of more than 30 nm. To demonstrate the performance of the new end station, Veber analysed individual cellulose microfibrils and imaged cell structures. All end stations are available to national and international user groups.
Funding information: Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung [grant No. project 05K19KH1 (SyMS)]; Germany's Excellence Strategy (grant No. EXC 2008-390540038 – UniSysCat).
arö
https://www.helmholtz-berlin.de/pubbin/news_seite?nid=26746;sprache=en
- Copy link
-
Sodium-ion batteries: New storage mechanism for cathode materials
Li-ion and Na-ion batteries operate through a process called intercalation, where ions are stored and exchanged between two chemically different electrodes. In contrast, co-intercalation, a process in which both ions and solvent molecules are stored simultaneously, has traditionally been considered undesirable due to its tendency to cause rapid battery failure. Against this traditional view, an international research team led by Philipp Adelhelm has now demonstrated that co-intercalation can be a reversible and fast process for cathode materials in Na-ion batteries. The approach of jointly storing ions and solvents in cathode materials provides a new handle for the designing batteries with high efficiency and fast charging capabilities. The results are published in Nature Materials.
-
Helmholtz Doctoral Award for Hanna Trzesniowski
During her doctoral studies at the Helmholtz Centre Berlin, Hanna Trzesniowski conducted research on nickel-based electrocatalysts for water splitting. Her work contributes to a deeper understanding of alkaline water electrolysis and paves the way for the development of more efficient and stable catalysts. On 8 July 2025, she received the Helmholtz Doctoral Prize, which honours the best and most original doctoral theses in the Helmholtz Association.
-
New department at HZB: ‘AI and Biomolecular Structures’
Since 1 July 2025, Dr. Andrea Thorn has been setting up the new AI and Biomolecular Structures department at HZB. A biophysicist with many years of experience in AI-based tools for structural biology, she is looking forward to collaborating closely with the macromolecular crystallography team at the MX beamlines of BESSY II.
