How to Flow Ultrathin Water Layers - A Liquid Flatjet for X-Ray Spectroscopy
Liquid flatjet system, showing the two nozzles from which two impinging single jets form a liquid water sheet with a thickness of 1 - 2 μm. © MBI
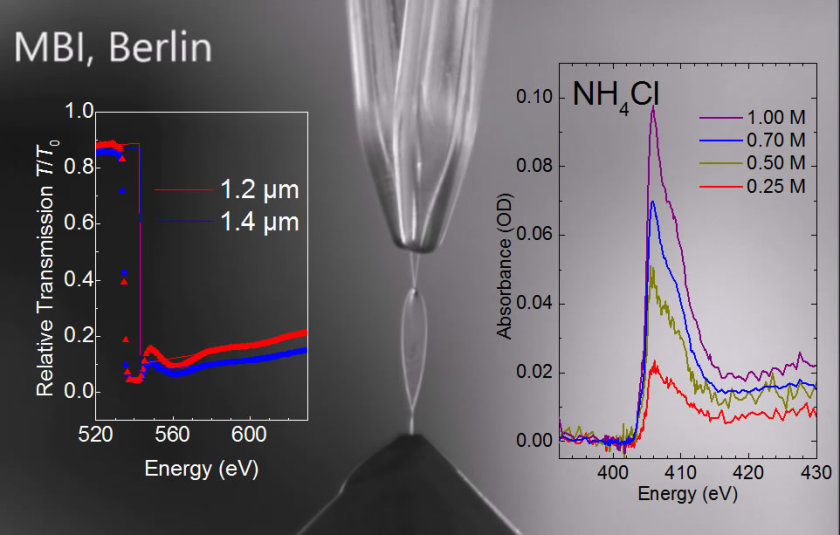
A collaboration between scientists from the Max Born Institute for Nonlinear Optics and Short Pulse Spectroscopy (MBI), the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (HZB) and the Max Planck Institute for Dynamics and Self-Organization (MPIDS) have now demonstrated the successful implementation of a liquid flatjet with a thickness in the μm range, allowing for XAS transmission measurements in the soft-x-ray regime. This paves the way for novel steady-state and time-resolved experiments.
A collaboration between scientists from the Max Born Institute for Nonlinear Optics and Short Pulse Spectroscopy (MBI), the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (HZB) and the Max Planck Institute for Dynamics and Self-Organization (MPIDS) have now demonstrated the successful implementation of a liquid flatjet with a thickness in the μm range, allowing for XAS transmission measurements in the soft-x-ray regime. This paves the way for novel steady-state and time-resolved experiments.
Here a phenomenon well known in the field of fluid dynamics has been applied: by obliquely colliding two identical laminar jets, the liquid expands radially, generating a sheet in the form of a leaf, bounded by a thicker rim, orthogonal to the plane of the impinging jets.
The novel aspect here is that a liquid water flatjet has been demonstrated with thicknesses in the few micrometer range, stable for tens to hundreds of minutes, fully operational under vacuum conditions (‹10-3mbar). For the first time, soft x-ray absorption spectra of a liquid sample could be measured in transmission without any membrane. The x-ray measurements were performed at the soft x-ray synchrotron facility BESSYII of the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin. This technological breakthrough opens up new frontiers in steady-state and time-resolved soft-x-ray spectroscopy of solution phase systems.
Read the full text at MBI.
Original publication: Structural Dynamics 2, 054301 (2015): A liquid flatjet system for solution phase soft-x-ray spectroscopy
Maria Ekimova, Wilson Quevedo, Manfred Faubel, Philippe Wernet, Erik T.J. Nibbering
Max-Born-Institut/red.
https://www.helmholtz-berlin.de/pubbin/news_seite?nid=14315;sprache=en
- Copy link
-
Protein crystallography at BESSY II: faster, better and more and more automatic
Many diseases are linked to malfunctions of proteins in the organism. The three-dimensional architecture of these molecules is often highly complex, but it can provide valuable insights into biological processes and the development of drugs. X-ray diffraction at the MX beamlines of BESSY II can be used to decipher the 3D structure of proteins. To date, more than 5000 structures have been solved at the three MX beamlines. Here, we present a review and an outlook with Manfred Weiss, head of the research group for macromolecular crystallography.
-
What Zinc concentration in teeth reveals
Teeth are composites of mineral and protein, with a bulk of bony dentin that is highly porous. This structure is allows teeth to be both strong and sensitive. Besides calcium and phosphate, teeth contain trace elements such as zinc. Using complementary microscopy imaging techniques, a team from Charité Berlin, TU Berlin and HZB has quantified the distribution of natural zinc along and across teeth in 3 dimensions. The team found that, as porosity in dentine increases towards the pulp, zinc concentration increases 5~10 fold. These results help to understand the influence of widely-used zinc-containing biomaterials (e.g. filling) and could inspire improvements in dental medicine.
-
Fascinating archaeological find becomes a source of knowledge
The Bavarian State Office for the Preservation of Historical Monuments (BLfD) has sent a rare artefact from the Middle Bronze Age to Berlin for examination using cutting-edge, non-destructive methods. It is a 3,400-year-old bronze sword, unearthed during archaeological excavations in Nördlingen, Swabia, in 2023. Experts have been able to determine how the hilt and blade are connected, as well as how the rare and well-preserved decorations on the pommel were made. This has provided valuable insight into the craft techniques employed in southern Germany during the Bronze Age. The BLfD used 3D computed tomography and X-ray diffraction to analyse internal stresses at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (HZB), as well as X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy at a BESSY II beamline supervised by the Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung (BAM).
