Titanium dioxide nanoreactor
The titanium dioxide nanoparticles crystallize in a polymer network at room temperature.
Tiny particles of titanium dioxide are found as key ingredients in wall paints, sunscreens, and toothpaste; they act as reflectors of light or as abrasives. However with decreasing particle size and a corresponding change in their surface-to-volume ratio, their properties change so that crystalline titanium dioxide nanoparticles acquire catalytic ability: Activated by the UV component in sunlight, they break down toxins or catalyze other relevant reactions.
Now, Dr. Katja Henzler and a team of chemists at the Helmholtz Centre Berlin have developed a synthesis to produce nanoparticles at room temperature in a polymer network. Their analysis, conducted at BESSY II, Berlin's synchrotron radiation source, has revealed the crystalline structure of the nanoparticles. This represents a major step forward in the usage of polymeric nanoreactors since, until recently, the nanoparticles had to be thoroughly heated to get them to crystallize. The last synthesis step can be spared due to the special environment inside the PNIPAM network.
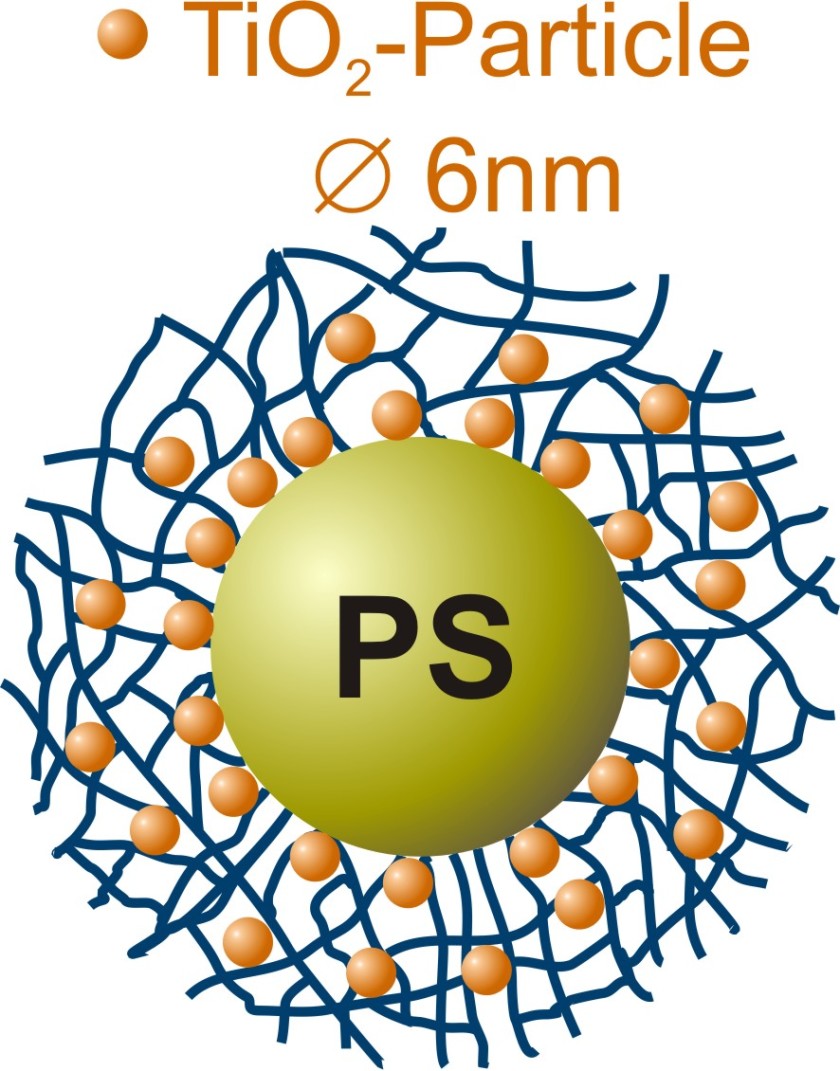
The Henzler team's polymeric nanoreactors consist of a polystyrene core surrounded by a network of PNIPAM chains. A titanium compound was added to an ethanolic solution of the polymer colloids, which did trigger the formation of small titanium dioxide particles within the PNIPAM network. The BESSY II experiments showed that the chemists were able to control the speed of these processes while at the same time affecting the quality of the nanocrystals that had formed.
Using the novel combination of x-ray microscopy and spectroscopy (NEXAFS-TXM, U41-SGM) at BESSY II, Henzler and the microscopy team were able to show that the nanoparticles are homogeneously distributed over the polymeric nanoreactors. The researchers examined their samples in a cryogenic aqueous environment, which prevents artifact formation due to sample drying. Their analysis showed that the nanoparticles have a crystalline structure. "The nanocrystals have a tetragonal anatase structure and this crystalline structure is a key to their catalytic performance. Additionally, our new analytic method allows us to control the quality of the synthesized particles so that we can optimize them for relevant applications," says Katja Henzler.
Nano Letters, 2013, 13 (2), pp 824–828;
DOI: 10.1021/nl3046798
https://www.helmholtz-berlin.de/pubbin/news_seite?nid=13668;sprache=en
- Copy link
-
Fascinating archaeological find becomes a source of knowledge
The Bavarian State Office for the Preservation of Historical Monuments (BLfD) has sent a rare artefact from the Middle Bronze Age to Berlin for examination using cutting-edge, non-destructive methods. It is a 3,400-year-old bronze sword, unearthed during archaeological excavations in Nördlingen, Swabia, in 2023. Experts have been able to determine how the hilt and blade are connected, as well as how the rare and well-preserved decorations on the pommel were made. This has provided valuable insight into the craft techniques employed in southern Germany during the Bronze Age. The BLfD used 3D computed tomography and X-ray diffraction to analyse internal stresses at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (HZB), as well as X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy at a BESSY II beamline supervised by the Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung (BAM).
-
Element cobalt exhibits surprising properties
The element cobalt is considered a typical ferromagnet with no further secrets. However, an international team led by HZB researcher Dr. Jaime Sánchez-Barriga has now uncovered complex topological features in its electronic structure. Spin-resolved measurements of the band structure (spin-ARPES) at BESSY II revealed entangled energy bands that cross each other along extended paths in specific crystallographic directions, even at room temperature. As a result, cobalt can be considered as a highly tunable and unexpectedly rich topological platform, opening new perspectives for exploiting magnetic topological states in future information technologies.
-
MXene for energy storage: More versatile than expected
MXene materials are promising candidates for a new energy storage technology. However, the processes by which the charge storage takes place were not yet fully understood. A team at HZB has examined, for the first time, individual MXene flakes to explore these processes in detail. Using the in situ Scanning transmission X-ray microscope 'MYSTIIC' at BESSY II, the scientists mapped the chemical states of Titanium atoms on the MXene flake surfaces. The results revealed two distinct redox reactions, depending on the electrolyte. This lays the groundwork for understanding charge transfer processes at the nanoscale and provides a basis for future research aimed at optimising pseudocapacitive energy storage devices.
