Corona research: Consortium of Berlin research and industry seeks active ingredients
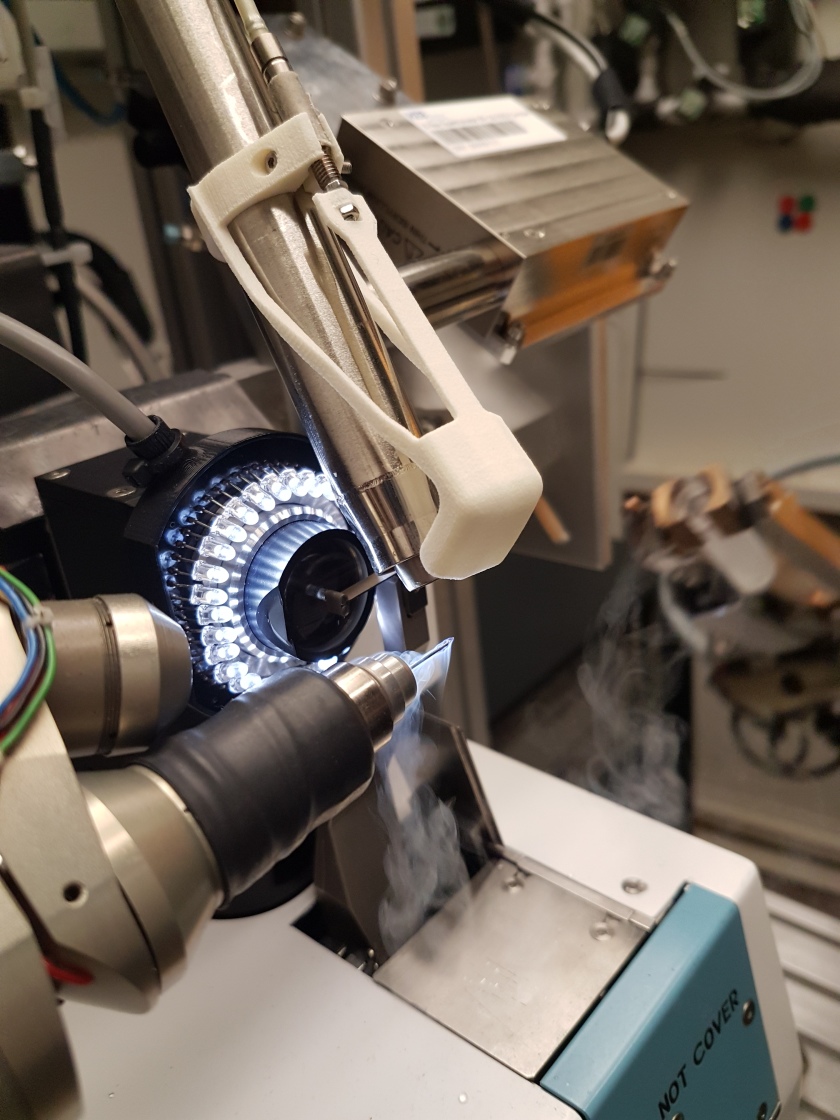
Protein crystals are analysed in the MX laboratory at BESSY II with hard X-rays. © C. Feiler/HZB
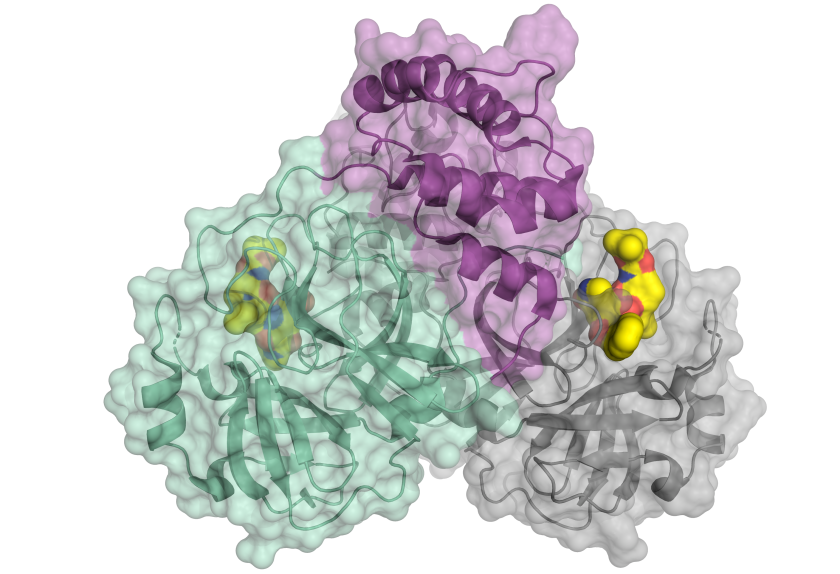
At BESSY II, Prof. Rolf Hilgenfeld (Uni Lübeck) was able to analyse an important protein of the SARS-CoV2 virus, the viral main protease which enables the virus to multiply. © H.Tabermann/HZB
The Berlin biotech company Molox GmbH and a team at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (HZB) have initiated a consortium of regional research groups and BASF. Together, they want to identify a starting point for the development of a potential active substance against the new coronavirus. Targets of potential inhibitors will be SARS-CoV2 proteins that promote the spread or infectivity of the viruses. Scientists from Freie Universität Berlin are also involved in the research work.
"Berlin combines important large-scale infrastructure with an excellent network of academic and industrial structural biologists and biochemists. The distances here are short, but resources and expertise must be strategically coordinated to be successful," says Dr. Holger von Moeller, the owner of the biotech company Molox.
Access to synchrotron radiation is essential for the success of the project. This particularly intense radiation is provided by the Berlin Electron Storage Ring for Synchrotron Radiation (BESSY II), which is operated by the HZB.
Several research groups at Freie Universität Berlin led by Prof. Markus Wahl, Prof. Christian Freund, Dr. Ursula Neu, and Prof. Sutapa Chakrabarti are working with Molox to produce the proteins and then crystallize them.
"The HZB is making all existing infrastructures available to the joint project," explains Dr. Manfred Weiss, head of the Research Group Macromolecular Crystallography (MX) at HZB.
BASF is the first project partner from the chemical industry to provide funds to start the investigations. Protein crystals will be saturated with potential inhibitors and subsequently analysed on the MX beamlines of BESSY II. In this way it can be discovered which compounds are particularly good at inhibiting the function of the protein - these should then be the starting points for the development of active substances.
The consortium is currently negotiating with other partners in order to acquire them and their substance libraries. "We are looking forward to this joint project and hope that we will be able to identify new potential active substances against SARS-CoV-2 very quickly", says Dr. Christian Feiler, project leader at HZB.
red.
https://www.helmholtz-berlin.de/pubbin/news_seite?nid=21283;sprache=en
- Copy link
-
What Zinc concentration in teeth reveals
Teeth are composites of mineral and protein, with a bulk of bony dentin that is highly porous. This structure is allows teeth to be both strong and sensitive. Besides calcium and phosphate, teeth contain trace elements such as zinc. Using complementary microscopy imaging techniques, a team from Charité Berlin, TU Berlin and HZB has quantified the distribution of natural zinc along and across teeth in 3 dimensions. The team found that, as porosity in dentine increases towards the pulp, zinc concentration increases 5~10 fold. These results help to understand the influence of widely-used zinc-containing biomaterials (e.g. filling) and could inspire improvements in dental medicine.
-
Fascinating archaeological find becomes a source of knowledge
The Bavarian State Office for the Preservation of Historical Monuments (BLfD) has sent a rare artefact from the Middle Bronze Age to Berlin for examination using cutting-edge, non-destructive methods. It is a 3,400-year-old bronze sword, unearthed during archaeological excavations in Nördlingen, Swabia, in 2023. Experts have been able to determine how the hilt and blade are connected, as well as how the rare and well-preserved decorations on the pommel were made. This has provided valuable insight into the craft techniques employed in southern Germany during the Bronze Age. The BLfD used 3D computed tomography and X-ray diffraction to analyse internal stresses at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (HZB), as well as X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy at a BESSY II beamline supervised by the Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung (BAM).
-
Element cobalt exhibits surprising properties
The element cobalt is considered a typical ferromagnet with no further secrets. However, an international team led by HZB researcher Dr. Jaime Sánchez-Barriga has now uncovered complex topological features in its electronic structure. Spin-resolved measurements of the band structure (spin-ARPES) at BESSY II revealed entangled energy bands that cross each other along extended paths in specific crystallographic directions, even at room temperature. As a result, cobalt can be considered as a highly tunable and unexpectedly rich topological platform, opening new perspectives for exploiting magnetic topological states in future information technologies.
