Future information technologies: 3D Quantum Spin Liquid revealed
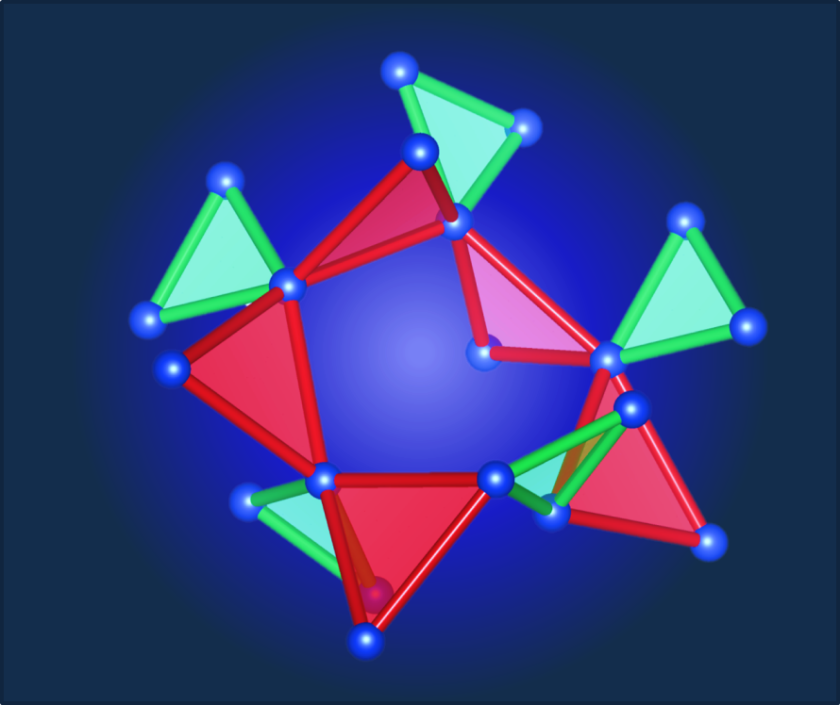
Two of the four magnetic interactions form a new three-dimensional network of corner-sharing triangles, known as the hyper-hyperkagome lattice, leading to the quantum spin liquid behavior in PbCuTe2O6. © HZB
Quantum Spin Liquids are candidates for potential use in future information technologies. So far, Quantum Spin Liquids have usually only been found in one or two dimensional magnetic systems only. Now an international team led by HZB scientists has investigated crystals of PbCuTe2O6 with neutron experiments at ISIS, NIST and ILL. They found spin liquid behaviour in 3D, due to a so called hyper hyperkagome lattice. The experimental data fit extremely well to theoretical simulations also done at HZB.
IT devices today are based on electronic processes in semiconductors. The next real breakthrough could be to exploit other quantum phenomena, for example interactions between tiny magnetic moments in the material, the so-called spins. So-called quantum-spin liquid materials could be candidates for such new technologies. They differ significantly from conventional magnetic materials because quantum fluctuations dominate the magnetic interactions: Due to geometric constraints in the crystal lattice, spins cannot all "freeze" together in a ground state - they are forced to fluctuate, even at temperatures close to absolute zero.
Quantum spin liquids: a rare phenomenon
Quantum spin liquids are rare and have so far been found mainly in two-dimensional magnetic systems. Three-dimensional isotropic spin liquids are mostly sought in materials where the magnetic ions form pyrochlore or hyperkagome lattices. An international team led by HZB physicist Prof. Bella Lake has now investigated samples of PbCuTe2O6, which has a three-dimensional lattice called hyper-hyperkagome lattice.
Magnetic interactions simulated
HZB physicist Prof. Johannes Reuther calculated the behaviour of such a three-dimensional hyper-hyperkagome lattice with four magnetic interactions and showed that the system exhibits quantum-spin liquid behaviour with a specific magnetic energy spectrum.
Experiments at neutron sources find 3D quantum spin liquid
With neutron experiments at ISIS, UK, ILL, France and NIST, USA the team was able to prove the very subtle signals of this predicted behaviour. "We were surprised how well our data fit into the calculations. This gives us hope that we can really understand what happens in these systems," explains first author Dr. Shravani Chillal, HZB.
arö
https://www.helmholtz-berlin.de/pubbin/news_seite?nid=21301;sprache=en
- Copy link
-
What Zinc concentration in teeth reveals
Teeth are composites of mineral and protein, with a bulk of bony dentin that is highly porous. This structure is allows teeth to be both strong and sensitive. Besides calcium and phosphate, teeth contain trace elements such as zinc. Using complementary microscopy imaging techniques, a team from Charité Berlin, TU Berlin and HZB has quantified the distribution of natural zinc along and across teeth in 3 dimensions. The team found that, as porosity in dentine increases towards the pulp, zinc concentration increases 5~10 fold. These results help to understand the influence of widely-used zinc-containing biomaterials (e.g. filling) and could inspire improvements in dental medicine.
-
Fascinating archaeological find becomes a source of knowledge
The Bavarian State Office for the Preservation of Historical Monuments (BLfD) has sent a rare artefact from the Middle Bronze Age to Berlin for examination using cutting-edge, non-destructive methods. It is a 3,400-year-old bronze sword, unearthed during archaeological excavations in Nördlingen, Swabia, in 2023. Experts have been able to determine how the hilt and blade are connected, as well as how the rare and well-preserved decorations on the pommel were made. This has provided valuable insight into the craft techniques employed in southern Germany during the Bronze Age. The BLfD used 3D computed tomography and X-ray diffraction to analyse internal stresses at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (HZB), as well as X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy at a BESSY II beamline supervised by the Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung (BAM).
-
Element cobalt exhibits surprising properties
The element cobalt is considered a typical ferromagnet with no further secrets. However, an international team led by HZB researcher Dr. Jaime Sánchez-Barriga has now uncovered complex topological features in its electronic structure. Spin-resolved measurements of the band structure (spin-ARPES) at BESSY II revealed entangled energy bands that cross each other along extended paths in specific crystallographic directions, even at room temperature. As a result, cobalt can be considered as a highly tunable and unexpectedly rich topological platform, opening new perspectives for exploiting magnetic topological states in future information technologies.
