Neutron instrument VSANS will move to Penn State University, USA
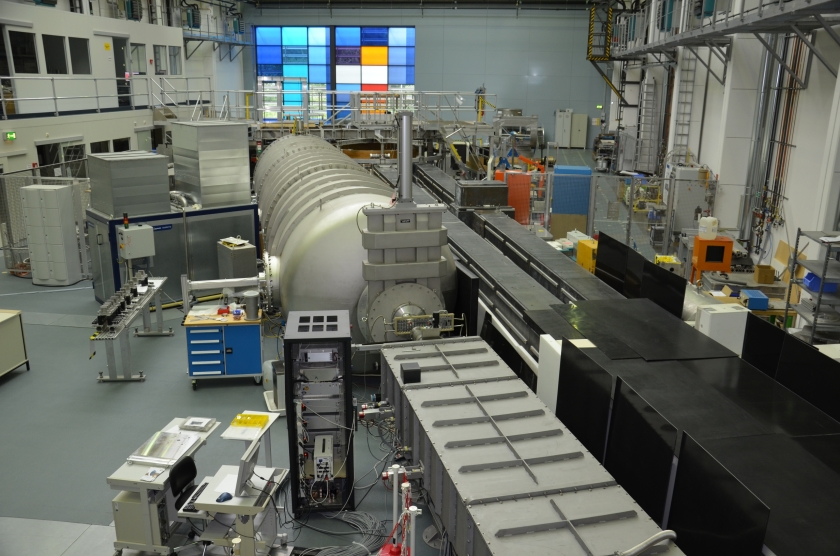
The VSANS instrument (here in the neutron hall at BER II) will move to Penn State University. © A. Kubatzki/HZB
At the end of 2019, the Berlin neutron source BER II was shut down as scheduled. To ensure that the high-quality instruments can continue to be used for research, they are moving to suitable neutron sources in Germany and abroad. Now, another move has been agreed upon: The Very Small Angle Scattering Instrument (VSANS) will find a new home at the Breazeale Research Reactor at Penn State University, USA, in spring 2022.
At Penn State University, the Radiation Science & Engineering Center (RSEC) operates the Breazeale reactor, which produces neutrons for research. An expansion is now planned there to accommodate the new, very large VSANS instrument.
VSANS stands for Very Small-Angle Neutron Scattering, i.e. the scattering of neutrons at very small scattering angles. This method enables insights into colloidal systems and soft matter, but also into glasses, biomimetic structural proteins, microemulsions, flexible electronics and many other questions, from physics to biology.
"Our goal is that our excellent instruments will continue to be available for research and innovation after BER II is shut down. We are therefore very pleased that the VSANS is being reinstalled at the Breazeale reactor", says Roland Steitz, HZB. This means that the HZB experts have now found a new location for almost all neutron instruments.
"The Breazeale reactor at the Penn State RSEC will be the only university research reactor with a SANS facility in the United States," says Kenan Ünlü, director of the RSEC and professor of nuclear engineering.
arö
https://www.helmholtz-berlin.de/pubbin/news_seite?nid=23155;sprache=en
- Copy link
-
MXene for energy storage: More versatile than expected
MXene materials are promising candidates for a new energy storage technology. However, the processes by which the charge storage takes place were not yet fully understood. A team at HZB has examined, for the first time, individual MXene flakes to explore these processes in detail. Using the in situ Scanning transmission X-ray microscope 'MYSTIIC' at BESSY II, the scientists mapped the chemical states of Titanium atoms on the MXene flake surfaces. The results revealed two distinct redox reactions, depending on the electrolyte. This lays the groundwork for understanding charge transfer processes at the nanoscale and provides a basis for future research aimed at optimising pseudocapacitive energy storage devices.
-
Compact electron accelerator for treating PFAS-contaminated water
So-called forever chemicals or PFAS compounds are a growing environmental problem. An innovative approach to treating PFAS-contaminated water and soil now comes from accelerator physics: high-energy electrons can break down PFAS molecules into harmless components through a process called radiolysis. A recent study published in PLOS One shows that an accelerator developed at HZB, based on a SRF photoinjector, can provide the necessary electron beam.
-
Bright prospects for tin perovskite solar cells
Perovskite solar cells are widely regarded as the next generation photovoltaic technology. However, they are not yet stable enough in the long term for widespread commercial use. One reason for this is migrating ions, which cause degradation of the semiconducting material over time. A team from HZB and the University of Potsdam has now investigated the ion density in four different, widely used perovskite compounds and discovered significant differences. Tin perovskite semiconductors produced with an alternative solvent had a particular low ion density — only one tenth that of lead perovskite semiconductors. This suggests that tin-based perovskites could be used to make solar cells that are not only really environmentally friendly but also very stable.
