Graphene on titanium carbide triggers a novel phase transition
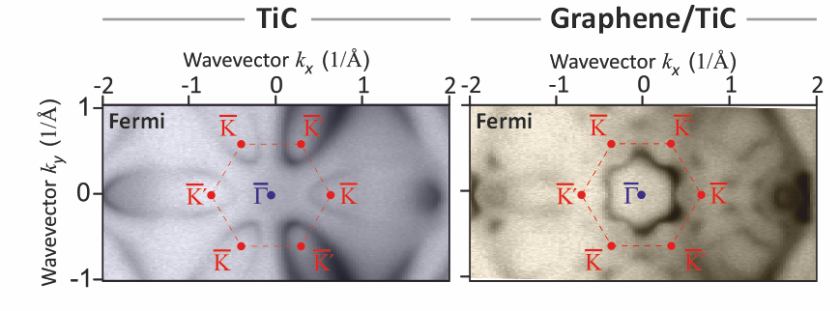
Graphene-induced Lifshitz-transition from a petal-shaped Fermi surface to a gear-shaped hole Fermi surface revealed by comparative full photoemission mapping of the band structures of bare TiC(111) and graphene/TiC(111). © HZB
Researchers have discovered a Lifshitz-transition in TiC, driven by a graphene overlayer, at the photon source BESSY II. Their study sheds light on the exciting potential of 2D materials such as graphene and the effects they can have on neighboring materials through proximity interactions.
Stacking 2D materials has garnered a lot of attention in recent years as it provides a unique opportunity to tailor material properties in a highly controllable manner. However, the influence of 2D materials on the properties of neighboring materials through proximity effects is not yet fully understood. In particular, very sensitive properties such as band gaps in semiconductors and excitonic properties have been observed to be influenced. Fermi surfaces of bulk metals have so far not been among the properties sensitive to a proximity effect.
The Fermi surface of a metal is a mathematical concept to represent the electrons of the highest energy in the material. Only these electrons participate in properties such as electrical conductivity. An important aspect of the Fermi surface is that it represents them in terms of the direction of their movement.
The new study by Andrei Varykhalov and his colleagues at BESSY II shows that a graphene layer can induce a Lifshitz transition in the near-surface region of an underlying metal, TiC: The Fermi surface transforms from a hole-like to an electron-like Fermi surface. The reported change in Fermi surface character is particularly relevant since it changes the orientation of the movement of the electrons and in the presence of a magnetic field it changes the orientation of the macroscopic electric current.
The present finding is an exciting development as it provides a new avenue for controlling and manipulating the electronic properties of materials, which has implications for a range of technological applications, for example designing materials with quantum properties such as high temperature superconductivity.
red.
https://www.helmholtz-berlin.de/pubbin/news_seite?nid=24892;sprache=en
- Copy link
-
What Zinc concentration in teeth reveals
Teeth are composites of mineral and protein, with a bulk of bony dentin that is highly porous. This structure is allows teeth to be both strong and sensitive. Besides calcium and phosphate, teeth contain trace elements such as zinc. Using complementary microscopy imaging techniques, a team from Charité Berlin, TU Berlin and HZB has quantified the distribution of natural zinc along and across teeth in 3 dimensions. The team found that, as porosity in dentine increases towards the pulp, zinc concentration increases 5~10 fold. These results help to understand the influence of widely-used zinc-containing biomaterials (e.g. filling) and could inspire improvements in dental medicine.
-
Fascinating archaeological find becomes a source of knowledge
The Bavarian State Office for the Preservation of Historical Monuments (BLfD) has sent a rare artefact from the Middle Bronze Age to Berlin for examination using cutting-edge, non-destructive methods. It is a 3,400-year-old bronze sword, unearthed during archaeological excavations in Nördlingen, Swabia, in 2023. Experts have been able to determine how the hilt and blade are connected, as well as how the rare and well-preserved decorations on the pommel were made. This has provided valuable insight into the craft techniques employed in southern Germany during the Bronze Age. The BLfD used 3D computed tomography and X-ray diffraction to analyse internal stresses at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (HZB), as well as X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy at a BESSY II beamline supervised by the Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung (BAM).
-
Element cobalt exhibits surprising properties
The element cobalt is considered a typical ferromagnet with no further secrets. However, an international team led by HZB researcher Dr. Jaime Sánchez-Barriga has now uncovered complex topological features in its electronic structure. Spin-resolved measurements of the band structure (spin-ARPES) at BESSY II revealed entangled energy bands that cross each other along extended paths in specific crystallographic directions, even at room temperature. As a result, cobalt can be considered as a highly tunable and unexpectedly rich topological platform, opening new perspectives for exploiting magnetic topological states in future information technologies.
