Details of a crucial reaction: Physicists uncover oxidation process of carbon monoxide on a ruthenium surface
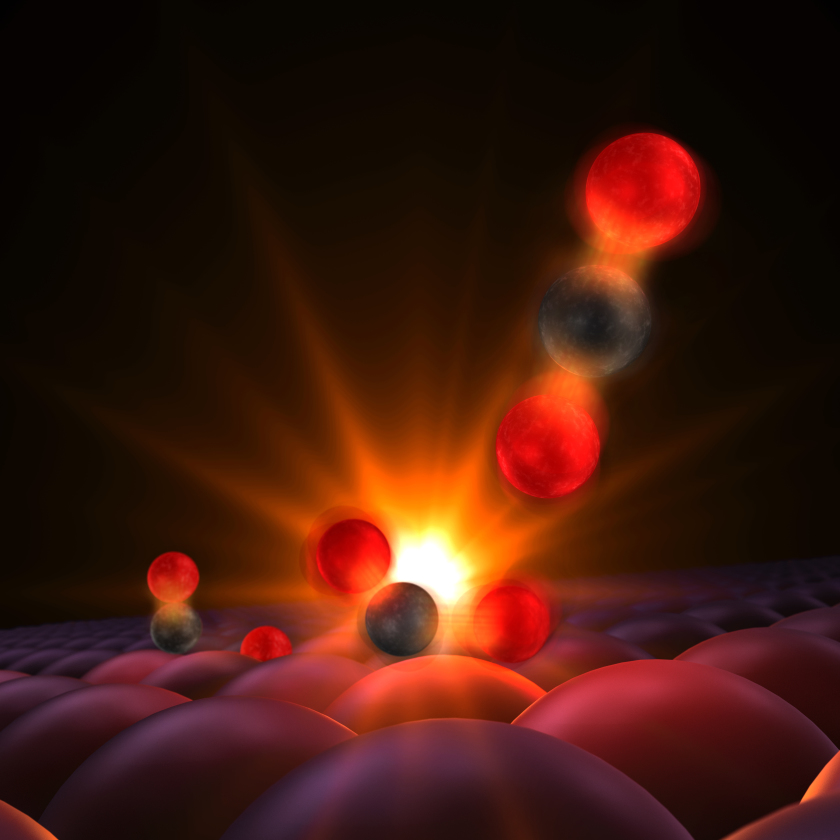
This illustrates a moment captured for the first time in experiments at SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory. The CO-molecule and oxygen-atoms are attached to the surface of a ruthenium catalyst. When hit with an optical laser pulse, the reactants vibrate and bump into each other and the carbon atom forms a transitional bond with the lone oxygen center. The resulting CO2 detaches and floats away. © SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory
An international team has observed the elusive intermediates that form when carbon monoxide is oxidized on a hot ruthenium metal surface. They used ultrafast X-ray and optical laser pulses at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, Menlo Park, California. The reaction between carbon monoxide and adsorbed oxygen atoms was initiated by heating the ruthenium surface with optical laser pulses. Directly afterwards, changes in the electronic structure of oxygen atoms were probed via X-ray absorption spectroscopy as they formed bonds with the carbon atoms.The observed transition states are consistent with density functional theory and quantum oscillator models.
The researchers were surprised to see so many of the reactants enter the transition state - and equally surprised to discover that only a small fraction of them go on to form stable carbon dioxide. The rest break apart again. "It's as if you are rolling marbles up a hill, and most of the marbles that make it to the top roll back down again," says Anders Nilsson, professor at the SLAC/Stanford SUNCAT Center for Interface Science and Catalysis and at Stockholm University, who led the research.
A team from the Institute of Methods and Instrumentation in Synchrotron Radiation Research from HZB has contributed in this research activities at SLAC sponsored by the Volkswagen-Foundation and the Helmholtz Virtual Institute “Dynamic Pathways in Multidimensional Landscapes” in which HZB and SLAC collaborate.
“These results help us to understand a really crucial reaction with high relevance for instance for environmental issues and to see which role catalysts may play”, Martin Beye of the HZB Team explains.
See full press release at SLAC-Website
Citation: H. Öström et al., Science, 12 February 2015 (10.1126/science.1261747)
arö/SLAC
https://www.helmholtz-berlin.de/pubbin/news_seite?nid=14141;sprache=en
- Copy link
-
Fascinating archaeological find becomes a source of knowledge
The Bavarian State Office for the Preservation of Historical Monuments (BLfD) has sent a rare artefact from the Middle Bronze Age to Berlin for examination using cutting-edge, non-destructive methods. It is a 3,400-year-old bronze sword, unearthed during archaeological excavations in Nördlingen, Swabia, in 2023. Experts have been able to determine how the hilt and blade are connected, as well as how the rare and well-preserved decorations on the pommel were made. This has provided valuable insight into the craft techniques employed in southern Germany during the Bronze Age. The BLfD used 3D computed tomography and X-ray diffraction to analyse internal stresses at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (HZB), as well as X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy at a BESSY II beamline supervised by the Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung (BAM).
-
Element cobalt exhibits surprising properties
The element cobalt is considered a typical ferromagnet with no further secrets. However, an international team led by HZB researcher Dr. Jaime Sánchez-Barriga has now uncovered complex topological features in its electronic structure. Spin-resolved measurements of the band structure (spin-ARPES) at BESSY II revealed entangled energy bands that cross each other along extended paths in specific crystallographic directions, even at room temperature. As a result, cobalt can be considered as a highly tunable and unexpectedly rich topological platform, opening new perspectives for exploiting magnetic topological states in future information technologies.
-
MXene for energy storage: More versatile than expected
MXene materials are promising candidates for a new energy storage technology. However, the processes by which the charge storage takes place were not yet fully understood. A team at HZB has examined, for the first time, individual MXene flakes to explore these processes in detail. Using the in situ Scanning transmission X-ray microscope 'MYSTIIC' at BESSY II, the scientists mapped the chemical states of Titanium atoms on the MXene flake surfaces. The results revealed two distinct redox reactions, depending on the electrolyte. This lays the groundwork for understanding charge transfer processes at the nanoscale and provides a basis for future research aimed at optimising pseudocapacitive energy storage devices.
