Invitation: Climate change - from knowledge to action
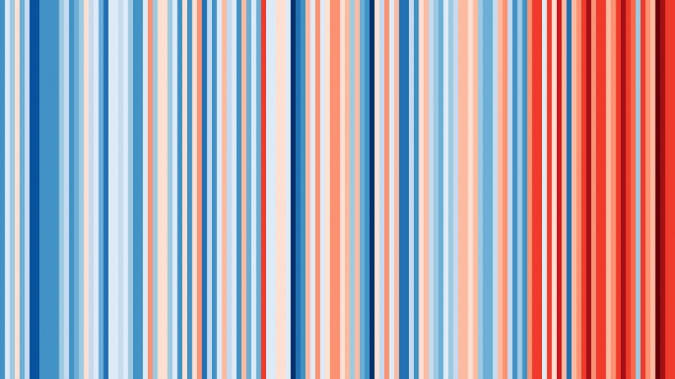
The graph visualizes the average temperature for Germany between 1881 and 2017; each strip stands for one year, based on the data set of the DWD. © Ed Hawkins/klimafakten.de
Climate change and its causes are undisputed. But how do we get from knowledge to action? What can science contribute to this? On Thursday, 5.12.2019 at 17:00 Clara Mayer (Fridays for Future), Volker Quaschning (HTW Berlin and Scientists for Future), Bernd Rech (scientific director of the HZB) and Kira Vinke (Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research) will discuss these questions. The event takes place in the Bunsen lecture hall of WISTA in Adlershof and is open to the public. Admission is free.
Countless scientific studies show how important it is to limit global warming. We must reduce greenhouse gas emissions at all levels of society and in all sectors in order to achieve our climate targets. But there are many hurdles to implementation. What can science do to speed up action here? Should science interfere at all?
These questions are discussed in an open debate. Participants are Clara Mayer from Fridays for Future, Prof. Volker Quaschning (HTW Berlin and Scientists for Future), Prof. Bernd Rech (Scientific Director of the HZB) and Dr. Kira Vinke of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research. The debate will be moderated by Rutger Schlatmann (Head of PVcomB at HZB).
The debate is open to the public and will take place in the Bunsen lecture hall of WISTA. Admission is free.
As the discussion takes place within the international user meeting at the HZB, the discussion language is English.
Venue: Bunsen Lecture Hall WISTA, Rudower Chaussee 17, 12489 Berlin
Time: Thursday, 5.12.2019 from 17:00 until 18:30
arö
https://www.helmholtz-berlin.de/pubbin/news_seite?nid=20908;sprache=en
- Copy link
-
MXene for energy storage: More versatile than expected
MXene materials are promising candidates for a new energy storage technology. However, the processes by which the charge storage takes place were not yet fully understood. A team at HZB has examined, for the first time, individual MXene flakes to explore these processes in detail. Using the in situ Scanning transmission X-ray microscope 'MYSTIIC' at BESSY II, the scientists mapped the chemical states of Titanium atoms on the MXene flake surfaces. The results revealed two distinct redox reactions, depending on the electrolyte. This lays the groundwork for understanding charge transfer processes at the nanoscale and provides a basis for future research aimed at optimising pseudocapacitive energy storage devices.
-
Bernd Rech elected to the BR50 Board of Directors
The Scientific Director at Helmholt-Zentrum Berlin is the new face behind the "Natural Sciences" unit at Berlin Research 50 (BR50). Following the election in December 2025, the constituent meeting of the new BR50 Board of Directors took place on 22 January 2026.
Its members are Michael Hintermüller (Weierstrass Institute, WIAS), Noa K. Ha (German Centre for Integration and Migration Research, DeZIM), Volker Haucke (Leibniz Research Institute for Molecular Pharmacology, FMP), Uta Bielfeldt (German Rheumatism Research Centre Berlin, DRFZ) and Bernd Rech (HZB).
-
A record year for our living lab for building-integrated PV
In 2025, our solar facade in Berlin-Adlershof generated more electricity than in any of the previous four years of operation.
