New interaction between light and matter discovered at BESSY II
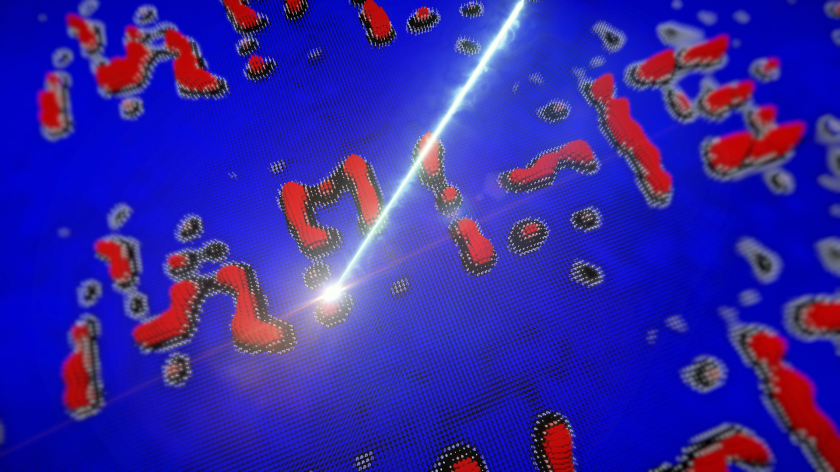
A bundled soft X-ray beam with a diameter of less than 50 nanometers writes numerous magnetic vortices, which together form the term "MPI-IS". © Alejandro Posada, Felix Groß/MPI-IS
A German-Chinese team led by Gisela Schütz from the MPI for Intelligent Systems has discovered a new interaction between light and matter at BESSY II. They succeeded in creating nanometer-fine magnetic vortices in a magnetic layer. These are so-called skyrmions, and candidates for future information technologies.
Skyrmions are 100 nanometre small three-dimensional structures that occur in magnetic materials. They resemble small coils: atomic elementary magnets - so-called spins - which are arranged in closed vortex structures. Skyrmions are topologically protected, i.e. their shape is unchangeable, and are therefore considered energy-efficient data storage devices.
Soft x-rays at BESSY II
In a series of experiments on the MAXYMUS beamline of BESSY II, the researchers have now shown that a bundled soft X-ray beam with a diameter of less than 50 nanometres can generate a magnetic vortex of 100 nanometres. In order to make the skyrmions visible, the researchers use the MAXYMUS scanning transmission X-ray microscope. This is a high-resolution X-ray microscope, weighing 1.8 tons, located at BESSY II.
Serendipitous discovery
This discovery was made by chance, as this type of interaction between light and matter was previously completely unknown. "We don't know how light writes matter," says Dr. Joachim Gräfe, head of the research group Nanomagnonics and Magnetization Dynamics at MPI-IS. He is one of the main authors of the study, which was published in Nature communications in February. "We can describe certain properties phenomenologically. We know that it has to do with the X-ray beam. It's not just an energy input like heat that writes the Skyrmion. It's really a resonant effect: we can directly excite the atoms responsible for magnetism." This enabled him and his team to write "MPI-IS" (see figure).
Outlook: Future Spintronics
The results are particularly relevant for the development and production of so-called spintronic data carriers, which store information in skyrmions. They are considered to be energy-efficient and less susceptible to interference. However, this development can only take its course if skyrmions can be created precisely and with a perfect fit - and this has now become possible for the first time. "Our goal is for X-rays to serve as a tool for determining or writing the arrangement of magnetic structures in the future."
red/MPI-IS
https://www.helmholtz-berlin.de/pubbin/news_seite?nid=21272;sprache=en
- Copy link
-
Fascinating archaeological find becomes a source of knowledge
The Bavarian State Office for the Preservation of Historical Monuments (BLfD) has sent a rare artefact from the Middle Bronze Age to Berlin for examination using cutting-edge, non-destructive methods. It is a 3,400-year-old bronze sword, unearthed during archaeological excavations in Nördlingen, Swabia, in 2023. Experts have been able to determine how the hilt and blade are connected, as well as how the rare and well-preserved decorations on the pommel were made. This has provided valuable insight into the craft techniques employed in southern Germany during the Bronze Age. The BLfD used 3D computed tomography and X-ray diffraction to analyse internal stresses at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (HZB), as well as X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy at a BESSY II beamline supervised by the Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung (BAM).
-
Element cobalt exhibits surprising properties
The element cobalt is considered a typical ferromagnet with no further secrets. However, an international team led by HZB researcher Dr. Jaime Sánchez-Barriga has now uncovered complex topological features in its electronic structure. Spin-resolved measurements of the band structure (spin-ARPES) at BESSY II revealed entangled energy bands that cross each other along extended paths in specific crystallographic directions, even at room temperature. As a result, cobalt can be considered as a highly tunable and unexpectedly rich topological platform, opening new perspectives for exploiting magnetic topological states in future information technologies.
-
MXene for energy storage: More versatile than expected
MXene materials are promising candidates for a new energy storage technology. However, the processes by which the charge storage takes place were not yet fully understood. A team at HZB has examined, for the first time, individual MXene flakes to explore these processes in detail. Using the in situ Scanning transmission X-ray microscope 'MYSTIIC' at BESSY II, the scientists mapped the chemical states of Titanium atoms on the MXene flake surfaces. The results revealed two distinct redox reactions, depending on the electrolyte. This lays the groundwork for understanding charge transfer processes at the nanoscale and provides a basis for future research aimed at optimising pseudocapacitive energy storage devices.
