User research at BESSY II: Graphite electrodes for rechargeable batteries investigated
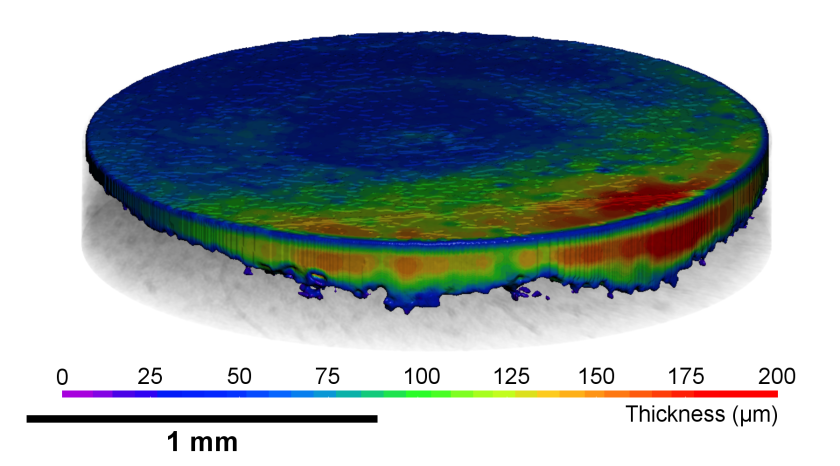
The tomogram during the charging process shows the spatially resolved changes in the graphite electrode thickness of a rechargeable aluminium ion battery in a discharged and charged state. © HZB
Rechargeable graphite dual ion batteries are inexpensive and powerful. A team of the Technical University of Berlin has investigated at the EDDI Beamline of BESSY II how the morphology of the graphite electrodes changes reversibly during cycling (operando). The 3D X-ray tomography images combined with simultaneous diffraction now allow a precise evaluation of the processes, especially of changes in the volume of the electrodes. This can help to further optimise graphite electrodes.
Published in Advanced Functional Materials (2020); Simultaneous X‐Ray Diffraction and Tomography Operando Investigation of Aluminum/Graphite Batteries; Giuseppe Antonio Elia, Giorgia Greco, Paul Hans Kamm, Francisco García‐Moreno, Simone Raoux, Robert Hahn
DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202003913
Abstract: Rechargeable graphite dual‐ion batteries are extremely appealing for grid‐level stationary storage of electricity, thanks to the low‐cost and high‐performance metrics, such as high‐power density, energy efficiency, long cycling life, and good energy density. An in‐depth understanding of the anion intercalation mechanism in graphite is fundamental for the design of highly efficient systems. In this work, a comparison is presented between pyrolytic (PG) and natural (NG) graphite as positive electrode materials in rechargeable aluminum batteries, employing an ionic liquid electrolyte. The two systems are characterized by operando synchrotron energy‐dispersive X‐ray diffraction and time‐resolved computed tomography simultaneously, establishing a powerful characterization methodology, which can also be applied more in general to carbon‐based energy‐related materials. A more in‐depth insight into the AlCl4−/graphite intercalation mechanism is obtained, evidencing a mixed‐staged region in the initial phase and a two‐staged region in the second phase. Moreover, strain analysis suggests a correlation between the irreversibility of the PG electrode and the increase of the inhomogenous strain. Finally, the imaging analysis reveals the influence of graphite morphology in the electrode volume expansion upon cycling.
red.
https://www.helmholtz-berlin.de/pubbin/news_seite?nid=22334;sprache=en
- Copy link
-
Element cobalt exhibits surprising properties
The element cobalt is considered a typical ferromagnet with no further secrets. However, an international team led by HZB researcher Dr. Jaime Sánchez-Barriga has now uncovered complex topological features in its electronic structure. Spin-resolved measurements of the band structure (spin-ARPES) at BESSY II revealed entangled energy bands that cross each other along extended paths in specific crystallographic directions, even at room temperature. As a result, cobalt can be considered as a highly tunable and unexpectedly rich topological platform, opening new perspectives for exploiting magnetic topological states in future information technologies.
-
MXene for energy storage: More versatile than expected
MXene materials are promising candidates for a new energy storage technology. However, the processes by which the charge storage takes place were not yet fully understood. A team at HZB has examined, for the first time, individual MXene flakes to explore these processes in detail. Using the in situ Scanning transmission X-ray microscope 'MYSTIIC' at BESSY II, the scientists mapped the chemical states of Titanium atoms on the MXene flake surfaces. The results revealed two distinct redox reactions, depending on the electrolyte. This lays the groundwork for understanding charge transfer processes at the nanoscale and provides a basis for future research aimed at optimising pseudocapacitive energy storage devices.
-
Bernd Rech elected to the BR50 Board of Directors
The Scientific Director at Helmholt-Zentrum Berlin is the new face behind the "Natural Sciences" unit at Berlin Research 50 (BR50). Following the election in December 2025, the constituent meeting of the new BR50 Board of Directors took place on 22 January 2026.
Its members are Michael Hintermüller (Weierstrass Institute, WIAS), Noa K. Ha (German Centre for Integration and Migration Research, DeZIM), Volker Haucke (Leibniz Research Institute for Molecular Pharmacology, FMP), Uta Bielfeldt (German Rheumatism Research Centre Berlin, DRFZ) and Bernd Rech (HZB).
