EU project CALIPSOplus has started for free access to European light sources
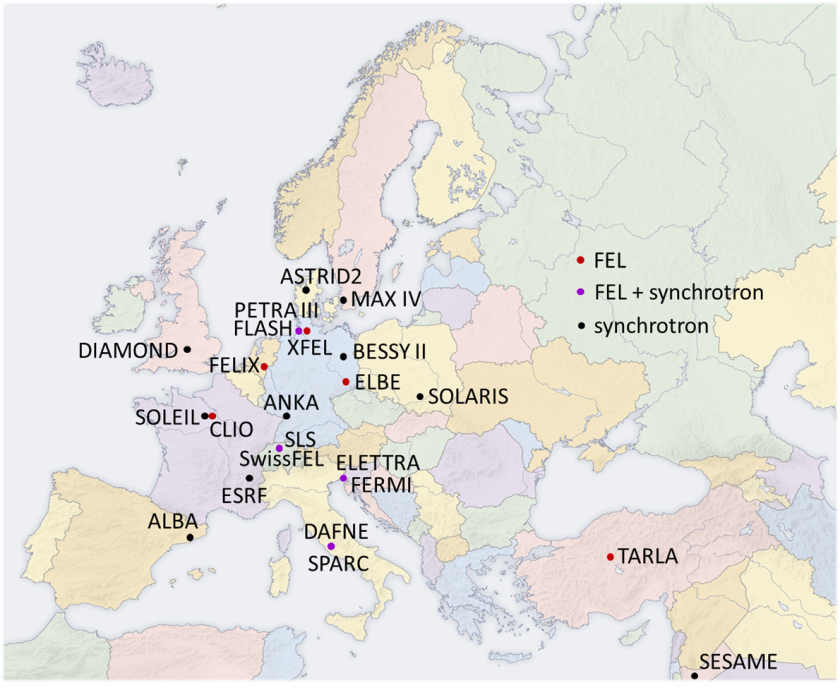
Light sources collaborating in CALIPSOplus
The EU is providing ten million euros in funding for the project CALIPSOplus, submitted by 19 European light sources. The project consortium, of which Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin is a member, kicked off on May 2017. CALIPSOplus is aimed at promoting the international exchange of scientists and transnational access to the light sources in Europe. Other priorities are to integrate the relatively less active regions of Europe and to initiate research projects with small and mid-sized companies.
CALIPSOplus has a runtime of four years and is coordinated by Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf. In the scope of CALIPSOplus, HZB manages the work package “Dissemination and Training” and is involved in the research project MOONPICS on the metrology of nanometre lenses.
The project partners will be taking targeted measures to advertise the outstanding analytical methods available here to researchers from Central and Eastern Europe who have so far rarely used the European light sources. This will help to integrate them more strongly into the European scientific landscape. “It is important that we approach the scientists from these countries in person, locally, and promote the opportunities at the light sources. So it’s great that the training programme is one of the priorities of CALIPSOplus,” says Dr. Antje Vollmer, who is coordinating the activities for HZB and who manages user coordination at HZB. Among other things, HZB is planning workshops at universities of the 13 youngest EU countries. Furthermore, there will be a “twinning and exchange programme” that will invite scientists from these countries to collaborate on an equal footing with experienced users of light sources.
The kick-off event for CALIPSOplus was held at Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) on 18 and 19 May 2017. More information
Website Wayforlight
Wayforlight.eu is currently being expanded and provides information about the experimental stations at Europe’s light sources and details on how to apply for measuring time.
(sz)
https://www.helmholtz-berlin.de/pubbin/news_seite?nid=14684;sprache=en
- Copy link
-
Fascinating archaeological find becomes a source of knowledge
The Bavarian State Office for the Preservation of Historical Monuments (BLfD) has sent a rare artefact from the Middle Bronze Age to Berlin for examination using cutting-edge, non-destructive methods. It is a 3,400-year-old bronze sword, unearthed during archaeological excavations in Nördlingen, Swabia, in 2023. Experts have been able to determine how the hilt and blade are connected, as well as how the rare and well-preserved decorations on the pommel were made. This has provided valuable insight into the craft techniques employed in southern Germany during the Bronze Age. The BLfD used 3D computed tomography and X-ray diffraction to analyse internal stresses at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (HZB), as well as X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy at a BESSY II beamline supervised by the Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung (BAM).
-
Element cobalt exhibits surprising properties
The element cobalt is considered a typical ferromagnet with no further secrets. However, an international team led by HZB researcher Dr. Jaime Sánchez-Barriga has now uncovered complex topological features in its electronic structure. Spin-resolved measurements of the band structure (spin-ARPES) at BESSY II revealed entangled energy bands that cross each other along extended paths in specific crystallographic directions, even at room temperature. As a result, cobalt can be considered as a highly tunable and unexpectedly rich topological platform, opening new perspectives for exploiting magnetic topological states in future information technologies.
-
MXene for energy storage: More versatile than expected
MXene materials are promising candidates for a new energy storage technology. However, the processes by which the charge storage takes place were not yet fully understood. A team at HZB has examined, for the first time, individual MXene flakes to explore these processes in detail. Using the in situ Scanning transmission X-ray microscope 'MYSTIIC' at BESSY II, the scientists mapped the chemical states of Titanium atoms on the MXene flake surfaces. The results revealed two distinct redox reactions, depending on the electrolyte. This lays the groundwork for understanding charge transfer processes at the nanoscale and provides a basis for future research aimed at optimising pseudocapacitive energy storage devices.
