Invitation: Climate change - from knowledge to action
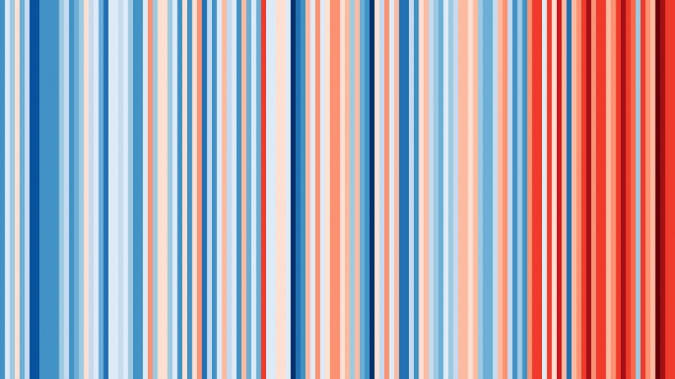
The graph visualizes the average temperature for Germany between 1881 and 2017; each strip stands for one year, based on the data set of the DWD. © Ed Hawkins/klimafakten.de
Climate change and its causes are undisputed. But how do we get from knowledge to action? What can science contribute to this? On Thursday, 5.12.2019 at 17:00 Clara Mayer (Fridays for Future), Volker Quaschning (HTW Berlin and Scientists for Future), Bernd Rech (scientific director of the HZB) and Kira Vinke (Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research) will discuss these questions. The event takes place in the Bunsen lecture hall of WISTA in Adlershof and is open to the public. Admission is free.
Countless scientific studies show how important it is to limit global warming. We must reduce greenhouse gas emissions at all levels of society and in all sectors in order to achieve our climate targets. But there are many hurdles to implementation. What can science do to speed up action here? Should science interfere at all?
These questions are discussed in an open debate. Participants are Clara Mayer from Fridays for Future, Prof. Volker Quaschning (HTW Berlin and Scientists for Future), Prof. Bernd Rech (Scientific Director of the HZB) and Dr. Kira Vinke of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research. The debate will be moderated by Rutger Schlatmann (Head of PVcomB at HZB).
The debate is open to the public and will take place in the Bunsen lecture hall of WISTA. Admission is free.
As the discussion takes place within the international user meeting at the HZB, the discussion language is English.
Venue: Bunsen Lecture Hall WISTA, Rudower Chaussee 17, 12489 Berlin
Time: Thursday, 5.12.2019 from 17:00 until 18:30
arö
-
BESSY II shows how solid-state batteries degrade
Solid-state batteries have several advantages: they can store more energy and are safer than batteries with liquid electrolytes. However, they do not last as long and their capacity decreases with each charge cycle. But it doesn't have to stay that way: Researchers are already on the trail of the causes. In the journal ACS Energy Letters, a team from HZB and Justus-Liebig-Universität, Giessen, presents a new method for precisely monitoring electrochemical reactions during the operation of a solid-state battery using photoelectron spectroscopy at BESSY II. The results help to improve battery materials and design.
-
HySPRINT Photovoltaics Lab inaugurated
After around four years of renovation, photovoltaics research groups moved into their offices in Kekuléstraße on 20 June 2024. With the reopening, the building has also been given a new name that makes the research more visible: it is now called HySPRINT Photovoltaics Lab.
-
Helmholtz Institute for Polymers in Energy Applications (HIPOLE Jena) Inaugurated
On June 17, 2024, the Helmholtz Institute for Polymers in Energy Applications (HIPOLE Jena) was officially inaugurated in Jena in the presence of Wolfgang Tiefensee, Minister for Economy, Science, and Digital Society of the Free State of Thuringia. The institute was founded by the Helmholtz Center Berlin for Materials and Energy (HZB) in cooperation with the Friedrich Schiller University Jena. It is dedicated to developing sustainable polymer materials for energy technologies, which are expected to play a key role in the energy transition and support Germany’s goal of becoming climate-neutral by 2045.
