New detector accelerates protein crystallography
60s on the new detector were sufficient to obtain the electron density of the PETase enzyme. © HZB
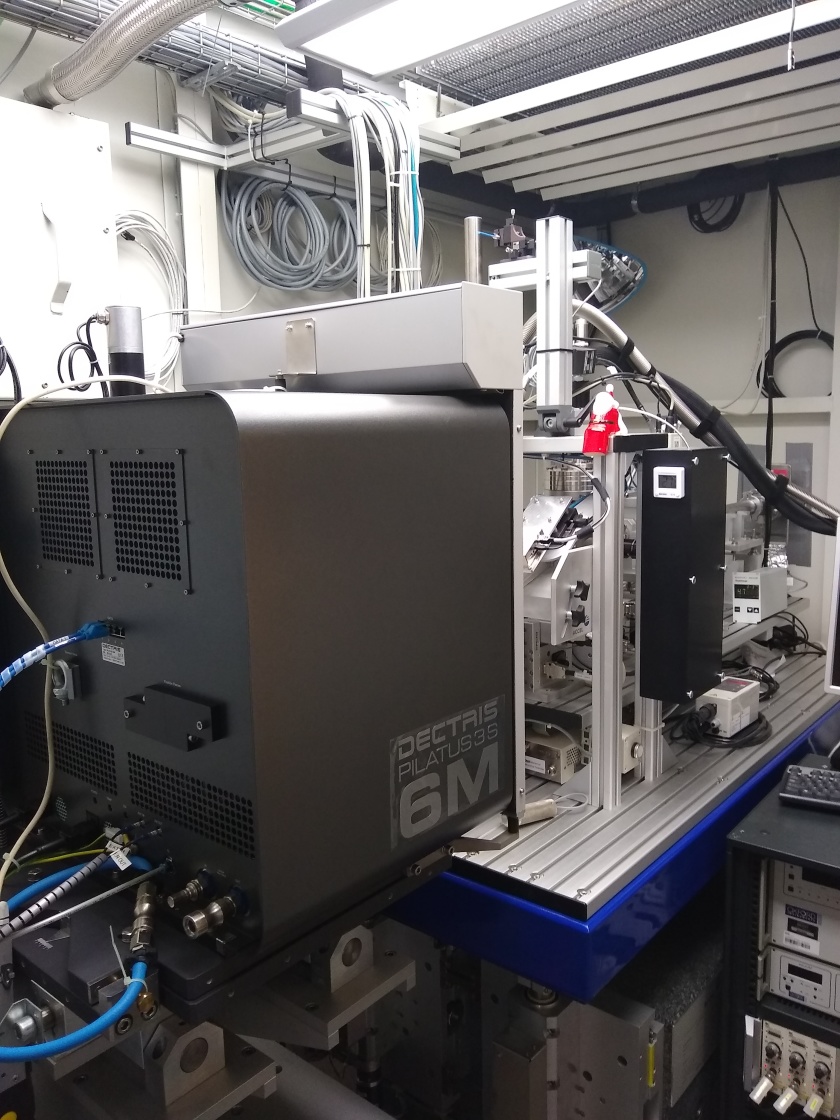

The MX-beamline 14.1 has been upgraded with a new, better, faster and more sensitive PILATUS-detector.
© HZB
Last week a new detector was installed at one of the three MX beamlines at HZB. Compared to the old detector the new one is better, faster and more sensitive. It allows to acquire complete data sets of complex proteins within a very short time.
Proteins consist of thousands of building blocks that can form complex architectures with folded or entangled regions. However, their shape plays a decisive role in the function of the protein in the organism. Using macromolecular crystallography at BESSY II, it is possible to decipher the architecture of protein molecules. For this purpose, tiny protein crystals are irradiated with X-ray light from the synchrotron source BESSY II. From the obtained diffraction patterns, the morphology of the molecules can be calculated.
Now the MX team at BESSY II has put a new detector into operation at the MX beamline 14.1, which works about 2 to 3 times faster than before. The team analysed a crystal from the enzyme PETase as a sample. PETase does partially degrade the plastic PET. In less than a minute, the detector was able to record a complete diffraction data set, which includes data from an angular range of 180 degrees. The data set consists of 1200 images, each of which was exposed to X-rays for 45 milliseconds. "The resulting electron density was of excellent quality and showed all structural features of the enzyme," explains Dr. Manfred Weiss, who leads the MX team at BESSY II.
The success of the HZB MX beamlines is documented by more than 3000 PDB entries from experimental beamtime from more than a hundred international user groups from academia and pharmaceutical research companies.
red.
-
A new way to control the magnetic properties of rare earth elements
The special properties of rare earth magnetic materials are due to the electrons in the 4f shell. Until now, the magnetic properties of 4f electrons were considered almost impossible to control. Now, a team from HZB, Freie Universität Berlin and other institutions has shown for the first time that laser pulses can influence 4f electrons- and thus change their magnetic properties. The discovery, which was made through experiments at EuXFEL and FLASH, opens up a new way to data storage with rare earth elements.
-
BESSY II shows how solid-state batteries degrade
Solid-state batteries have several advantages: they can store more energy and are safer than batteries with liquid electrolytes. However, they do not last as long and their capacity decreases with each charge cycle. But it doesn't have to stay that way: Researchers are already on the trail of the causes. In the journal ACS Energy Letters, a team from HZB and Justus-Liebig-Universität, Giessen, presents a new method for precisely monitoring electrochemical reactions during the operation of a solid-state battery using photoelectron spectroscopy at BESSY II. The results help to improve battery materials and design.
-
HZB magazine lichtblick - the new issue is out!
In his search for the perfect catalyst, HZB researcher Robert Seidel is now getting a tailwind – thanks to a ERC Consolidator Grant. In the cover story, we explain why the X-ray source BESSY II plays an important role for his research.
