Long night of Sciences at HZB: Experience science up close!
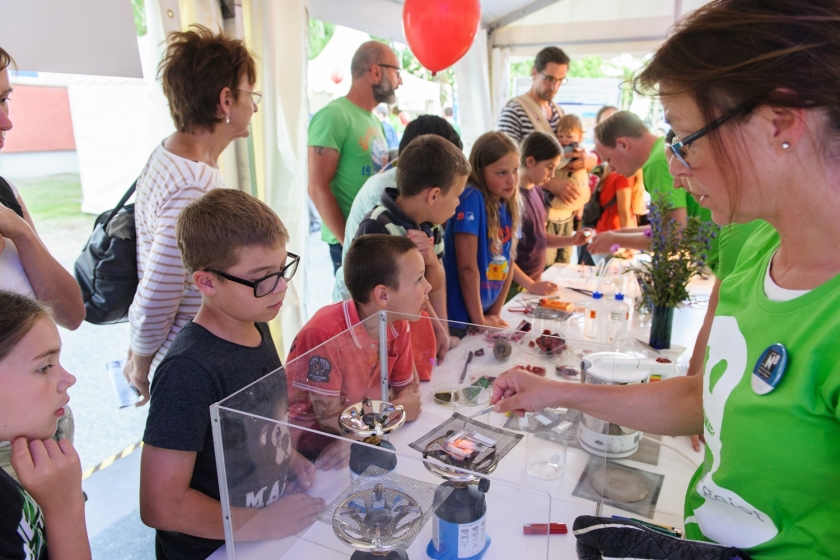

Can you make solar cells from fruit tea? You can find out how at the Long Night of the Sciences. © HZB/P. Dera
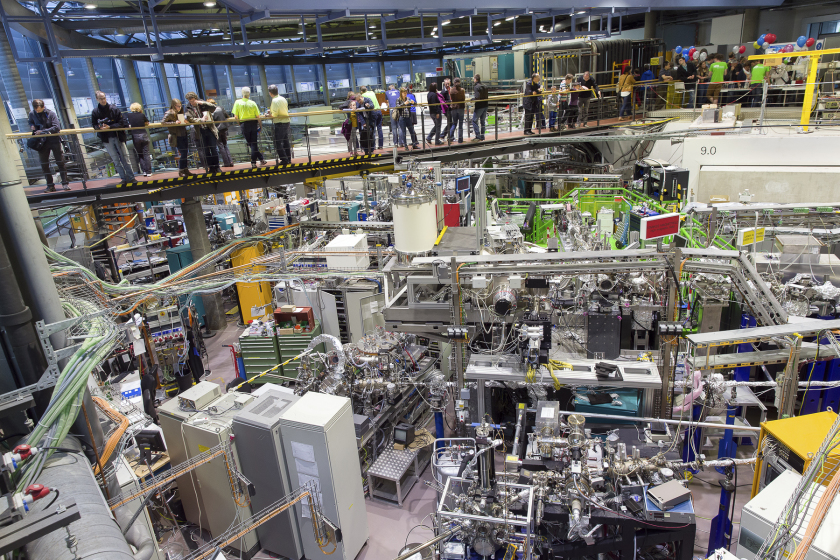
Come by and be surprised: Take a look at the accelerator BESSY II during the Long Night of the Sciences. © HZB/M. Setzpfandt
Important info: At the HZB, FFP2 masks are mandatory indoors from the age of 14 during this event.
How can solar cells be produced even more efficiently? Why is "green" hydrogen so important for our future? Why does Berlin need an accelerator to screen materials? The answers are available at the Long Night of the Sciences. On July 2, 2022, 5 p.m. to midnight, HZB opens its doors at the Adlershof site and invites young and old to experiment.
Our researchers will discover new energy materials and develop technologies for a climate-neutral energy supply - a topic that is more topical than ever. Ask us what you always wanted to know about renewable energy. There will be opportunities to do so at the booths or at the lectures on the "Road of Energy" (located at Kekuléstraße) as well as at the panel discussion "No energy transition without hydrogen" at 7 pm in the BESSY lecture hall. We are looking forward to the dialog with you!
We cordially invite you to visit our electron accelerator BESSY II. It provides intense light to develop new solar cells, batteries or catalysts. On a tour through the accelerator you will find out why electrons race in circles at almost the speed of light. Children can participate in a scavenger hunt through the accelerator or experiment in the school lab.
About 100 meters away, at our location in Kekuléstraße 5, photovoltaics experts are setting up an outdoor energy street. There you can experience what working in the lab is like. Among other things, you can build your own solar cells from toothpaste and fruit tea or come to the "Temple of Solar Cells".
Programme
Further information and the exact times of the programme offers mentioned here can be found on our website:
- Programme around BESSY II: Albert-Einstein-Str. 15
- Programme Road of Energy: Kekuléstr. 5
- Info about tickets
- website Long Night of Sciences
Please bring an FFP2 mask for your visit to HZB. Due to the pandemic and construction measures, the number of visitors in the BESSY building will be limited. We ask for your understanding if there are waiting times in front of the building. Thank you very much!
(sz)
https://www.helmholtz-berlin.de/pubbin/news_seite?nid=23866;sprache=en
- Copy link
-
MXene for energy storage: More versatile than expected
MXene materials are promising candidates for a new energy storage technology. However, the processes by which the charge storage takes place were not yet fully understood. A team at HZB has examined, for the first time, individual MXene flakes to explore these processes in detail. Using the in situ Scanning transmission X-ray microscope 'MYSTIIC' at BESSY II, the scientists mapped the chemical states of Titanium atoms on the MXene flake surfaces. The results revealed two distinct redox reactions, depending on the electrolyte. This lays the groundwork for understanding charge transfer processes at the nanoscale and provides a basis for future research aimed at optimising pseudocapacitive energy storage devices.
-
Compact electron accelerator for treating PFAS-contaminated water
So-called forever chemicals or PFAS compounds are a growing environmental problem. An innovative approach to treating PFAS-contaminated water and soil now comes from accelerator physics: high-energy electrons can break down PFAS molecules into harmless components through a process called radiolysis. A recent study published in PLOS One shows that an accelerator developed at HZB, based on a SRF photoinjector, can provide the necessary electron beam.
-
Bright prospects for tin perovskite solar cells
Perovskite solar cells are widely regarded as the next generation photovoltaic technology. However, they are not yet stable enough in the long term for widespread commercial use. One reason for this is migrating ions, which cause degradation of the semiconducting material over time. A team from HZB and the University of Potsdam has now investigated the ion density in four different, widely used perovskite compounds and discovered significant differences. Tin perovskite semiconductors produced with an alternative solvent had a particular low ion density — only one tenth that of lead perovskite semiconductors. This suggests that tin-based perovskites could be used to make solar cells that are not only really environmentally friendly but also very stable.
